- What Is Skin Xenografting?
- Key Steps in Skin Xenografting
- Mechanisms of HCMV Impact on Skin Xenografts
- Understanding Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)
- Megan Loyd
- The Role of Immunosuppression in Skin Xenografts
- Key Contributions by Megan Loyd in Xenograft and HCMV Research
- Technological Advancements in Skin Xenografts
- Future Innovations
- Addressing Ethical and Practical Concerns
- Practical Measures to Prevent HCMV Infections in Xenograft Patients
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What role does Megan Loyd play in skin xenograft research?
- How does HCMV affect skin xenografts?
- What are the technological advancements in skin xenografts?
- What ethical considerations are associated with skin xenografts?
- What are the clinical applications of skin xenografts?
- How do immunosuppressive treatments impact skin xenografts?
- What are the challenges in managing HCMV in skin xenografts?
Skin Xenograft HCMV Megan Loyd, specifically involving human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), has emerged as a pivotal area of research in transplant medicine.
These procedures, where skin is transplanted from one species to another, such as from animals to humans, offer unique insights into immune responses, skin diseases, and potential treatments. Megan Loyd, a leading researcher in this field, has significantly advanced our understanding of HCMV’s impact on skin xenografts.
This article will delve into the complexities of skin xenograft HCMV Megan Loyd, exploring its challenges, mechanisms, and potential solutions.
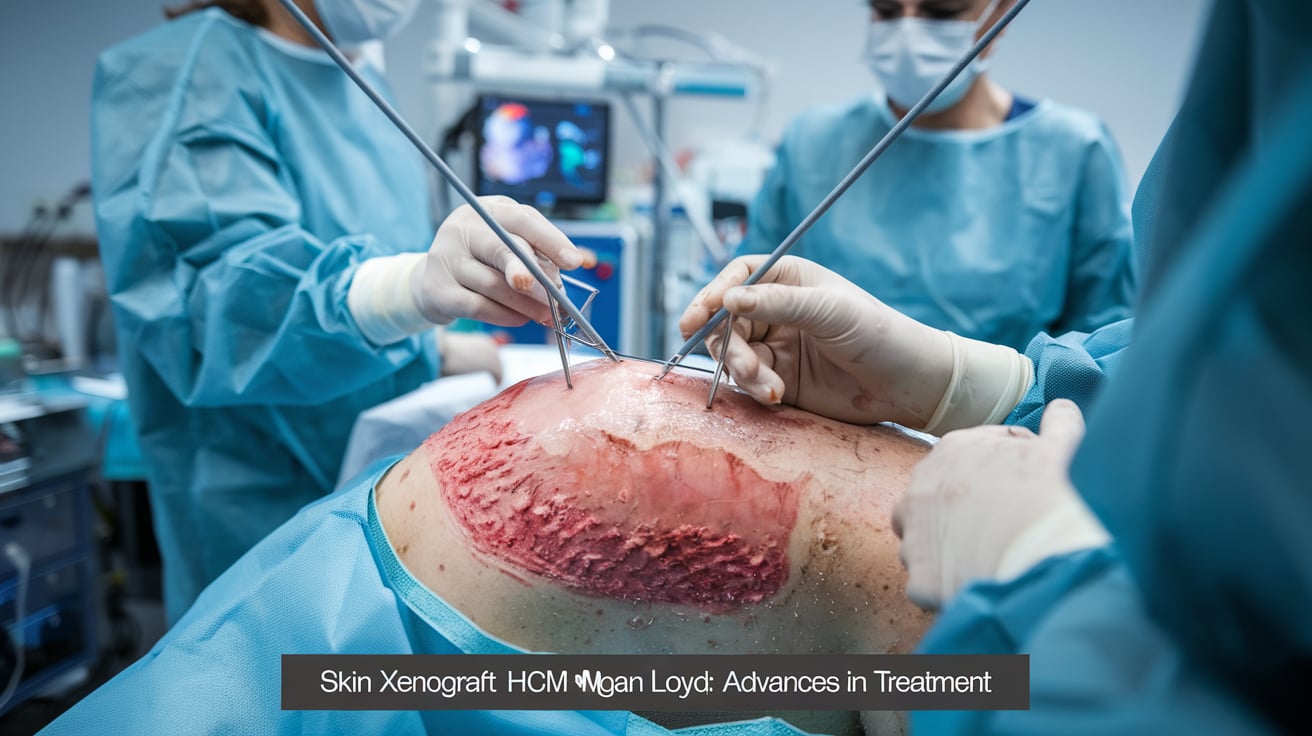
What Is Skin Xenografting?
A skin xenograft involves transplanting skin tissue between different species, typically from animals (like pigs or primates) to humans.
This innovative approach allows researchers to model human skin reactions to infections, drugs, and immune responses that are otherwise difficult to replicate in lab settings. Megan Loyd’s work in this area has been instrumental in establishing skin xenografts as a viable model for studying human skin biology.
The primary goal is to improve transplant success rates and treatment outcomes for skin disorders and burns.
Key Steps in Skin Xenografting
- Selection of Donor Skin: High-quality animal skin, usually from pigs, is selected because of its similar structure to human skin.
- Preparation and Sterilization: The donor skin undergoes thorough preparation, including sterilization, to reduce the risk of contamination and infection.
- Application to the Wound: Surgeons carefully place the graft over the damaged area, ensuring a snug fit to maximize the chances of success and minimize complications.
Mechanisms of HCMV Impact on Skin Xenografts
HCMV affects skin xenografts through several mechanisms. It can damage cells directly, induce inflammation, and disrupt the immune response in the grafted skin.
These factors contribute to the heightened risk of graft rejection and complications. Megan Loyd’s studies have highlighted the molecular pathways through which HCMV exerts its effects.
By identifying these mechanisms, Loyd is paving the way for targeted therapeutic strategies that could mitigate HCMV’s impact and improve skin xenograft outcomes.
Understanding Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV)
Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is a common virus that typically remains dormant in healthy individuals. However, in patients with compromised immune systems—like those receiving immunosuppressive drugs—HCMV can become active, posing severe risks.
In the context of skin xenografting, HCMV infections can exacerbate immune rejection, intensify inflammation, and even lead to graft failure.
Megan Loyd
Megan Loyd, a renowned researcher in the field of xenografting, has conducted groundbreaking studies on the interactions between HCMV and immune responses in xenografts.
Her research has illuminated the mechanisms by which HCMV accelerates graft rejection and identified potential antiviral strategies to counter these effects.
This work is crucial, as it offers the possibility of reducing the need for long-term immunosuppressive therapy, ultimately helping patients experience fewer complications.
The Role of Immunosuppression in Skin Xenografts
Immunosuppressive therapy plays a crucial role in preventing graft rejection in skin xenografts.
However, it also increases the risk of infections like HCMV, complicating the balance between preventing rejection and safeguarding against infections.
Megan Loyd’s research investigates how different immunosuppressive regimens interact with HCMV and their implications for graft success.
Her work aims to optimize these treatments, ensuring they are effective without compromising the immune response too much, thus enhancing the safety and success of skin xenografts.
Key Contributions by Megan Loyd in Xenograft and HCMV Research
Understanding the Immune Response
Megan Loyd’s research has improved our understanding of how HCMV affects the immune response to xenografts, providing insights into why the body often rejects foreign skin.
Antiviral Strategies
Loyd has pioneered the study of antiviral medications that could be used specifically to prevent HCMV activation in immunosuppressed patients.
Optimizing Immunosuppression
Loyd’s studies focus on minimizing the levels of immunosuppressive drugs required by xenograft patients, reducing the risks of HCMV infection while maintaining graft acceptance.
Technological Advancements in Skin Xenografts
Advancements in medical technology are revolutionizing the field of skin xenografts. 3D bioprinting and gene-editing tools like CRISPR-Cas9 are enabling more precise transplantations and reducing the risk of complications.
Megan Loyd’s research incorporates these technological innovations to refine xenograft procedures, making them safer and more effective.
These advancements improve the success rates of skin xenografts and expand their applications in treating severe skin disorders and chronic wounds.
Future Innovations
Advancements in bioengineering and genetic modification are opening new possibilities in skin grafting, making xenografts safer and more compatible with the human body.
Researchers are now exploring genetically modified pig skin that is less likely to trigger immune responses. In addition, 3D printing technologies and bioengineered skin grafts are paving the way for highly customized solutions that could reduce the need for immunosuppression entirely.
Bioengineered Skin Grafts
With bioengineering, scientists aim to create skin grafts that closely resemble human skin, reducing the risk of rejection.
3D Printing in Grafting
3D printing technology allows for the creation of skin grafts tailored to fit a patient’s wound precisely, further enhancing graft success rates and reducing complications.
Genetic Modifications to Reduce Rejection
Genetic engineering in animals aims to modify donor skin at the cellular level, creating grafts that are “immune-friendly” and less likely to be rejected by human bodies.
Addressing Ethical and Practical Concerns
While xenografting offers life-saving potential, it also raises ethical considerations, particularly concerning the use of animal tissues.
Medical regulations worldwide are evolving to address these concerns, balancing the need to save human lives with the ethical implications of using animal donors.
Practical Measures to Prevent HCMV Infections in Xenograft Patients
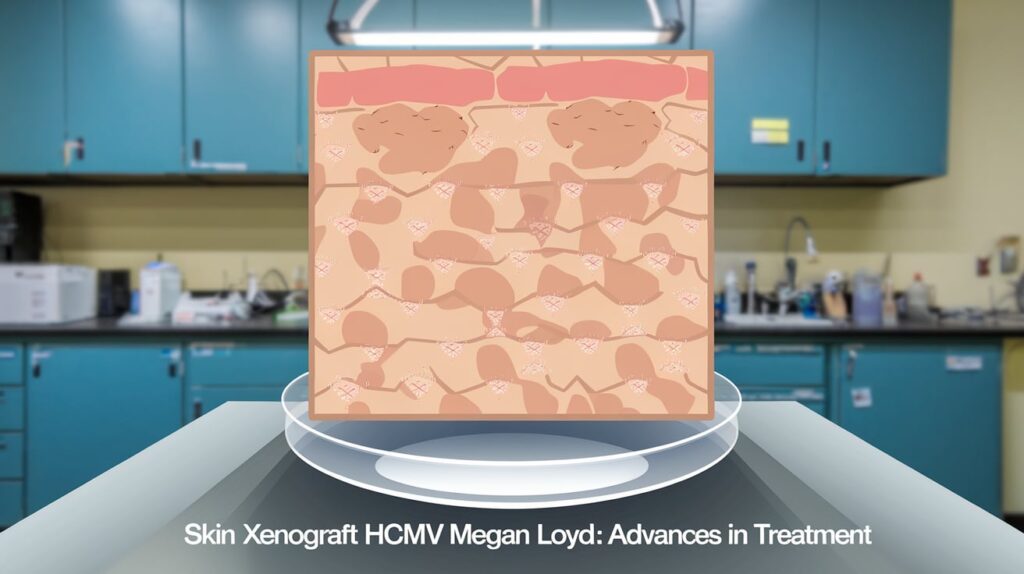
To address the risks posed by HCMV, medical professionals are exploring multiple strategies:
Antiviral Medications
Preventive antiviral treatments are being developed and tested to keep HCMV in check for immunosuppressed patients.
Enhanced Screening and Monitoring
Screening for HCMV in both donor and recipient tissues helps identify risks early, while post-surgical monitoring ensures any viral activation is detected and managed quickly.
Conclusion
Megan Loyd’s contributions to skin xenografts, particularly in managing HCMV, have been transformative. Her research enhances our understanding of how HCMV impacts xenografts and drives the development of strategies to mitigate these effects.
As researchers continue to innovate and refine skin xenograft procedures, Megan Loyd’s work sets the stage for more effective and widely applicable treatments in transplant medicine.
FAQs
What role does Megan Loyd play in skin xenograft research?
Megan Loyd is a key researcher in the field of skin xenografts, particularly focusing on understanding the impact of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) on these procedures. Her work aims to improve transplant outcomes and manage viral complications.
How does HCMV affect skin xenografts?
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) can significantly complicate skin xenograft success by impairing the immune response, increasing the risk of graft rejection, and causing complications. Megan Loyd’s research is dedicated to finding ways to mitigate these effects.
What are the technological advancements in skin xenografts?
Technological advancements like 3D bioprinting and CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing are revolutionizing skin xenograft procedures. These innovations enhance precision and safety, allowing for more effective transplantations.
What ethical considerations are associated with skin xenografts?
Ethical considerations in skin xenografts involve balancing the use of animal tissues with patient safety. Megan Loyd’s research adheres to strict ethical guidelines to ensure responsible and safe use of transgenic tissues.
What are the clinical applications of skin xenografts?
Skin xenografts are used in treating severe skin conditions, burns, and chronic wounds. They provide temporary skin coverage, allowing patients to heal naturally or wait for human donor skin.
How do immunosuppressive treatments impact skin xenografts?
Immunosuppressive therapies are crucial for preventing graft rejection in skin xenografts but can increase the risk of infections like HCMV. Megan Loyd’s research aims to optimize these treatments to enhance graft survival without compromising the immune system.
What are the challenges in managing HCMV in skin xenografts?
Managing HCMV in skin xenografts is challenging due to its ability to impair the immune response and cause complications. Megan Loyd’s research focuses on developing strategies to control HCMV’s impact and improve transplant success rates.